1.问题
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 后序 遍历 。
示例 1
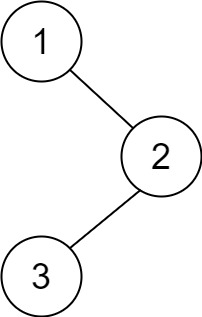
"图1"
输入:root = [1,null,2,3]
输出:[3,2,1]
示例 2
输入:root = []
输出:[]
示例 3
输入:root = [1]
输出:[1]
提示:
- 树中节点的数目在范围 [0, 100] 内
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
2.解题思路
二叉树的后序遍历规则:左-右-根,解题思路其实和前面两篇【LeetCode】144.二叉树的前序遍历差不太多.
2.1 递归
定义函数 postOrderTraversal(root)为遍历root节点。则调用顺序为:
postOrderTraversal(root.left); postOrderTraversal(root.right); root.val;复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是二叉搜索树的节点数。每一个节点恰好被遍历一次。
空间复杂度:O(n),为递归过程中栈的开销,平均情况下为 O(logn),最坏情况下树呈现链状,为 O(n)。
2.2 迭代
1) 遍历root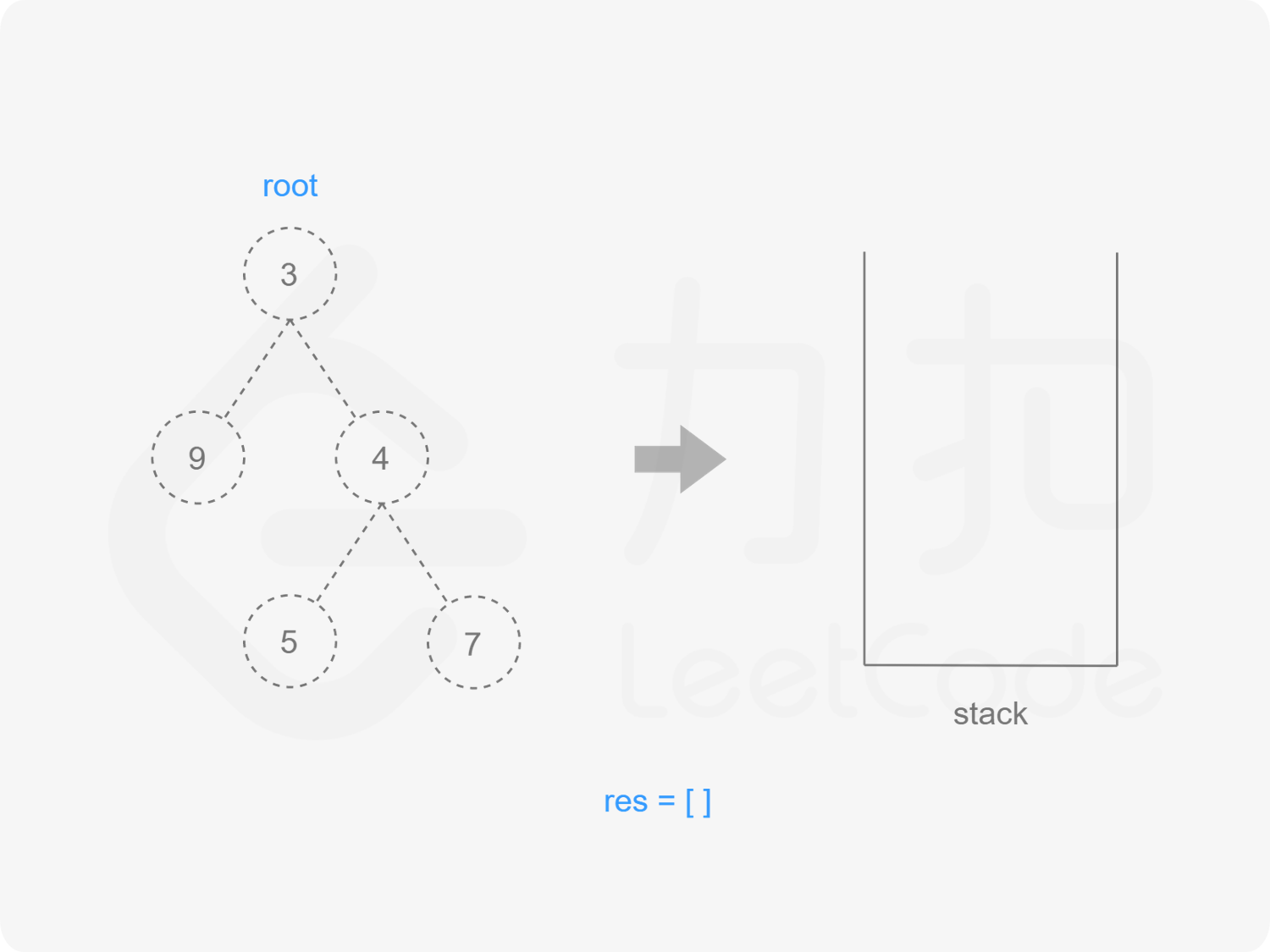
"图2"
2) root入栈
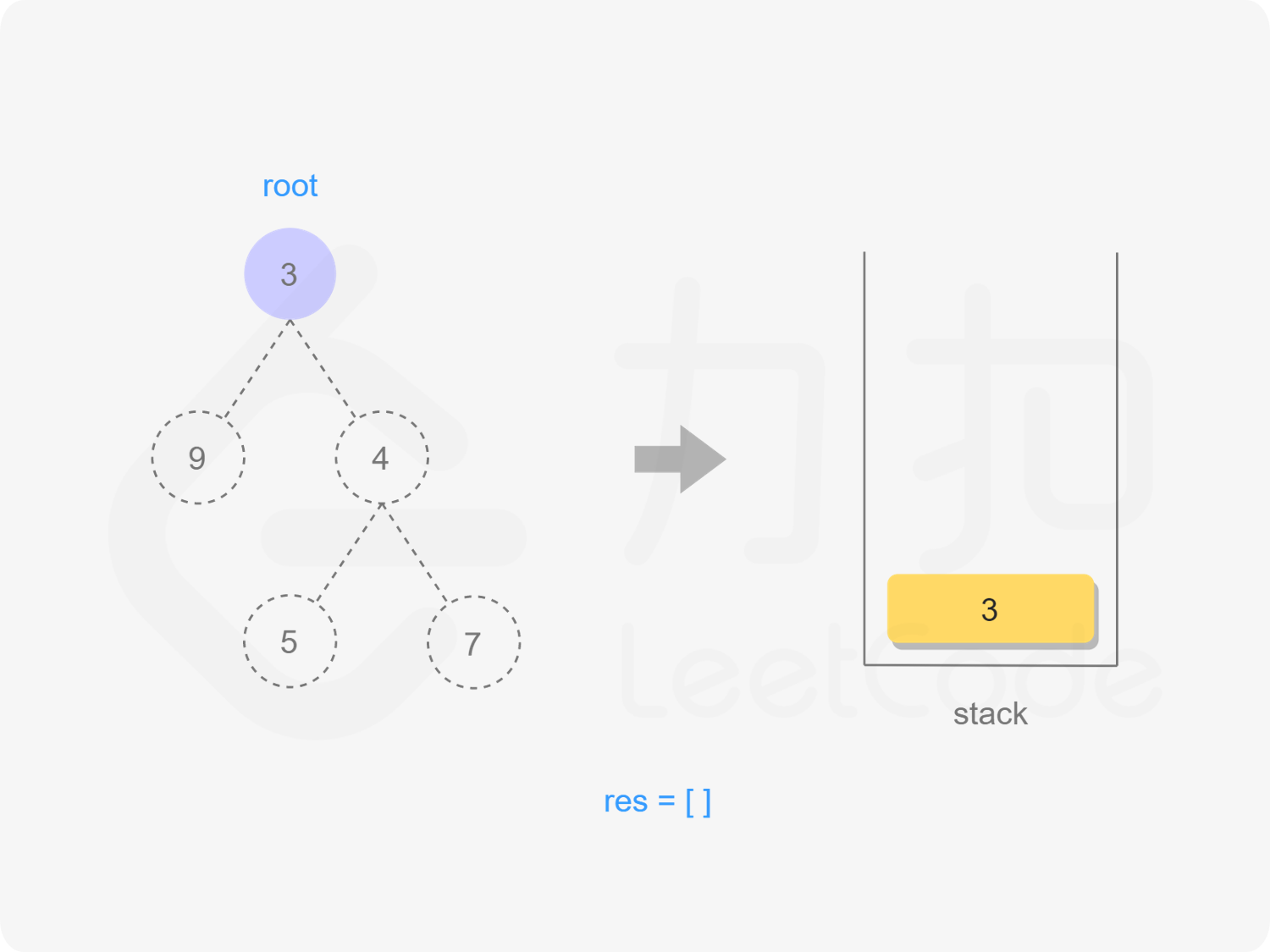
"图3"
3)root.left入栈
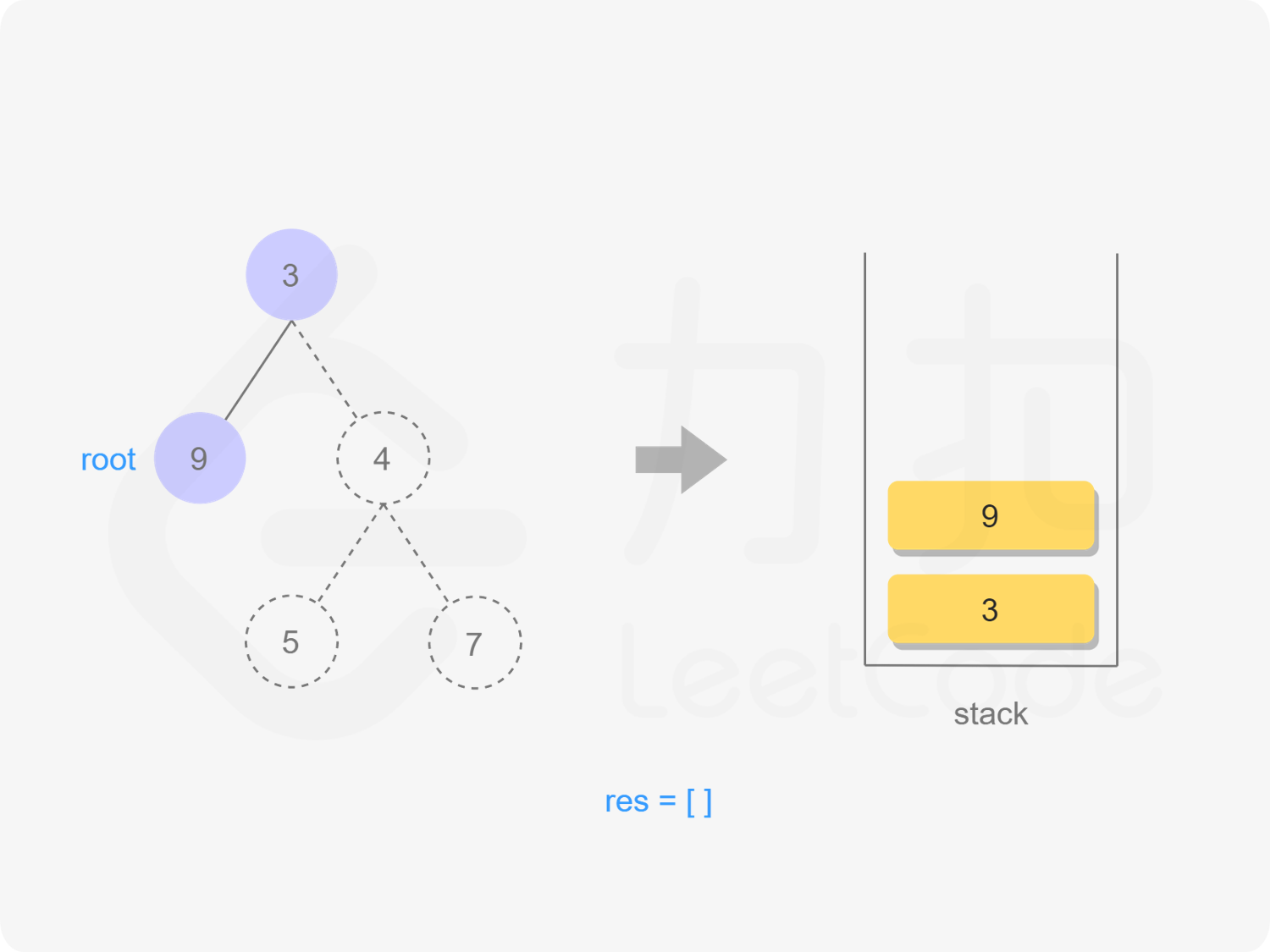
"图4"
4)root.left再无左子树了,左子树根节点出栈,遍历,并标记当前出栈的节点为已访问过,否则遍历、入栈root.right
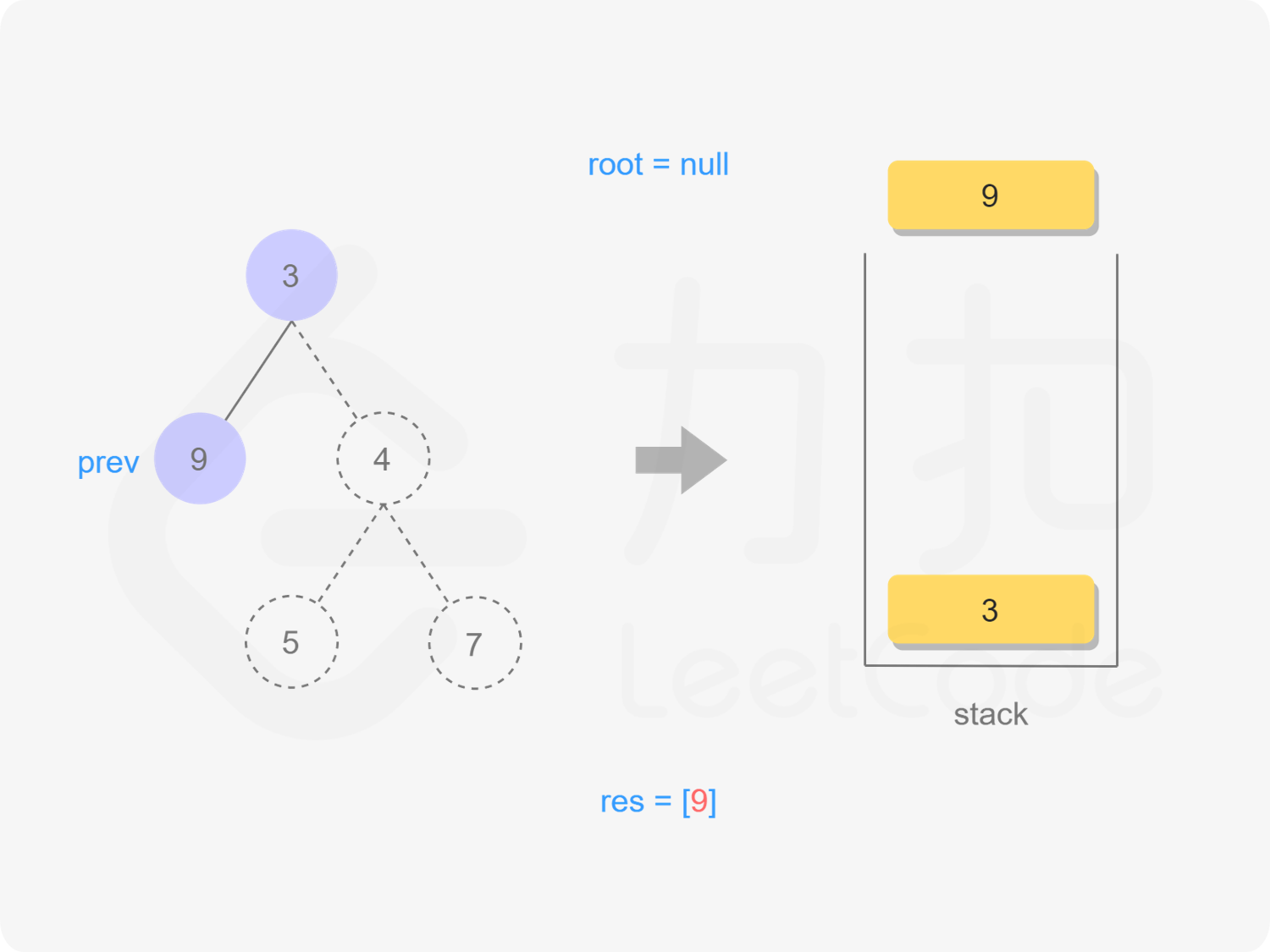
"图5"
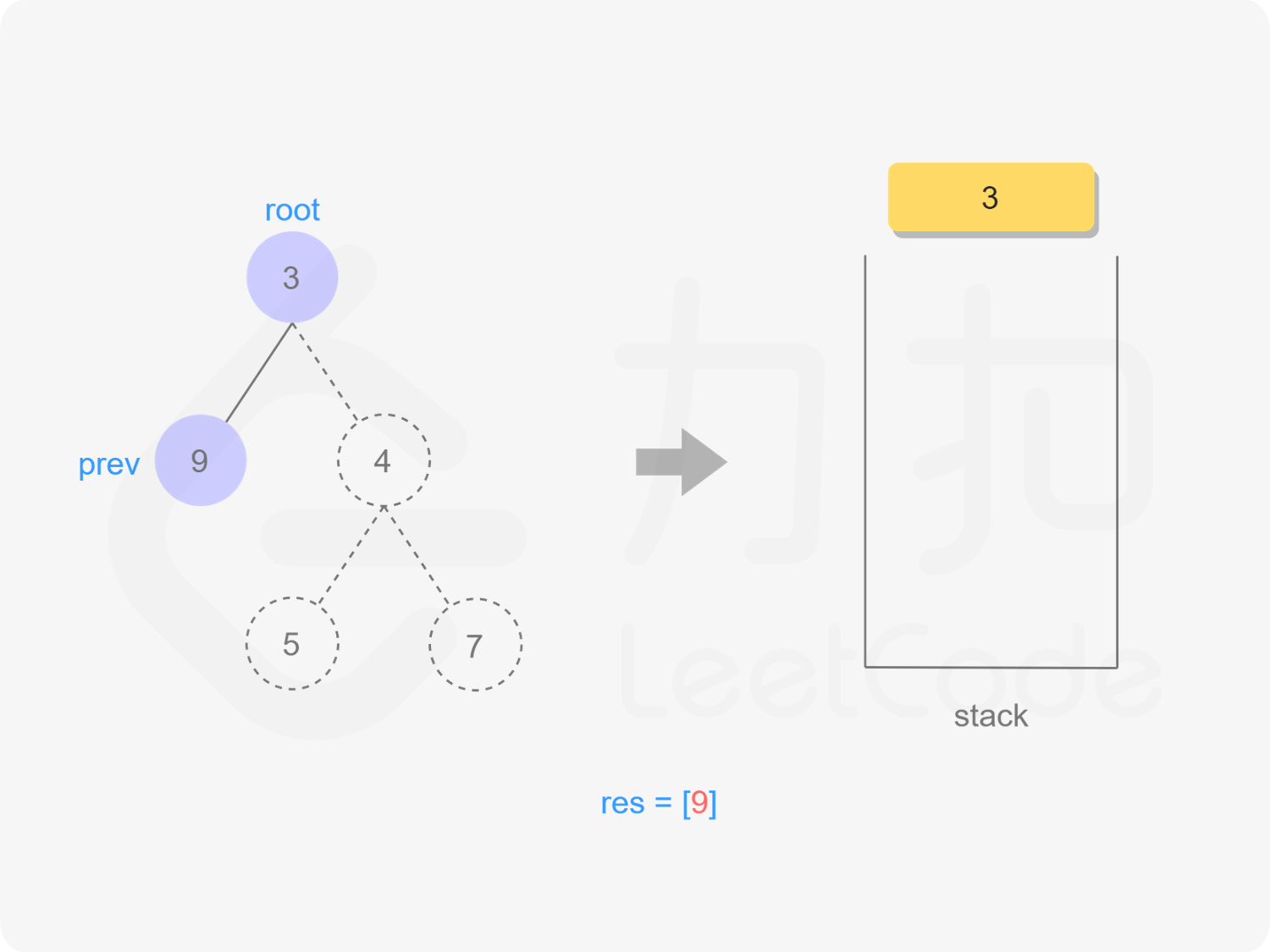
"图6"
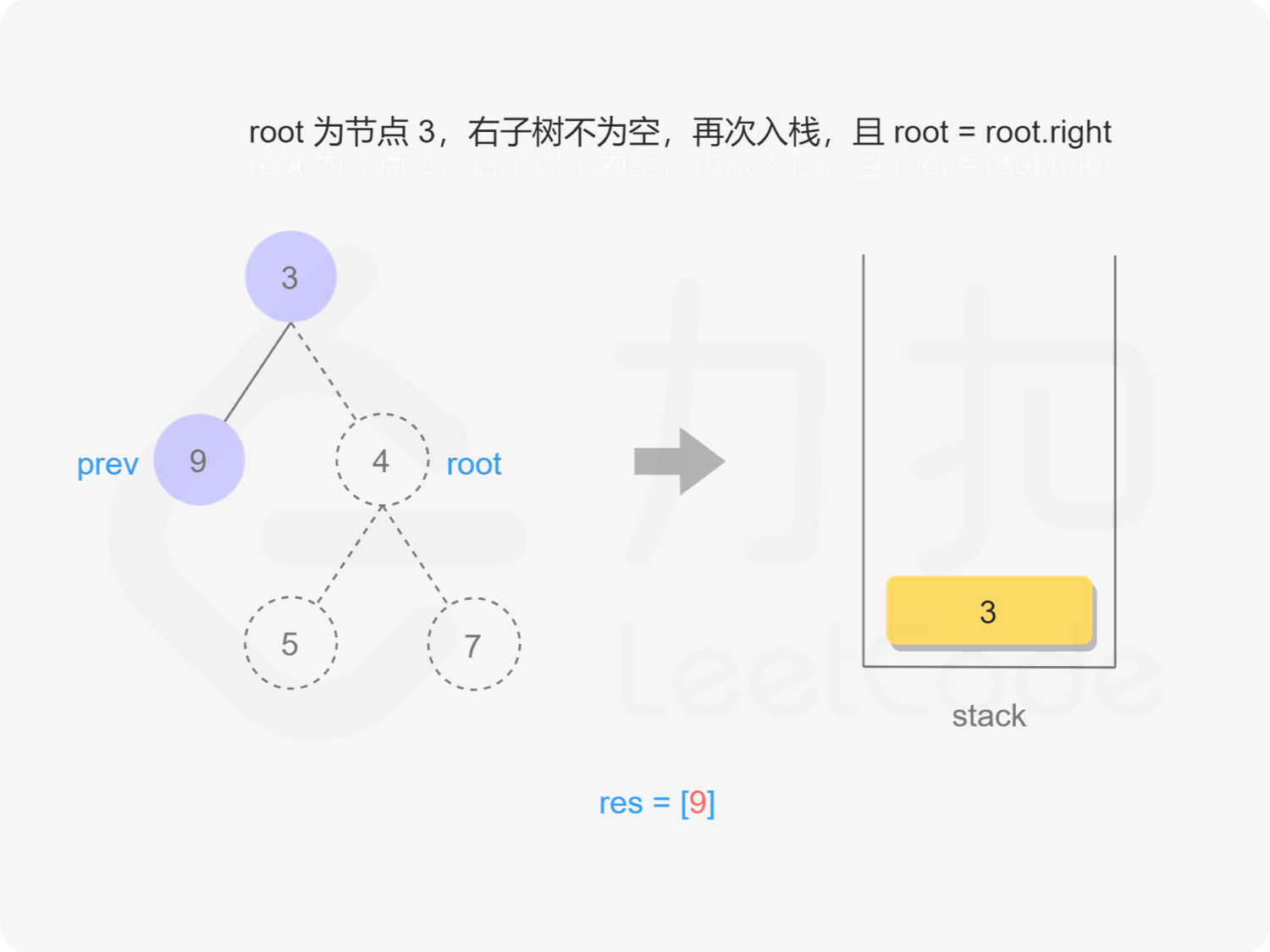
"图7"
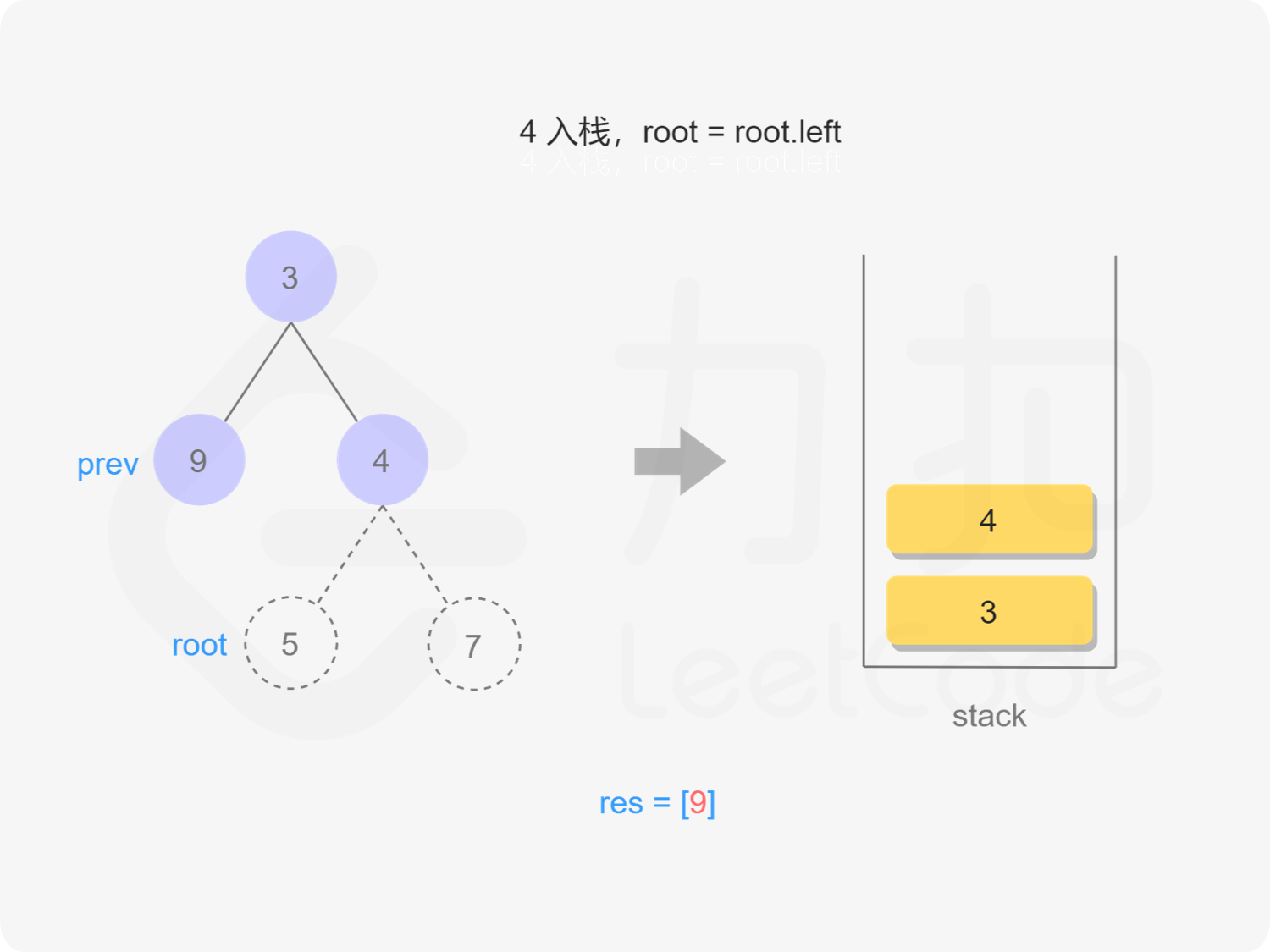
"图8"
5)同理,先把4所有左节点入栈,到达最左节点后,出栈,遍历val,标记当前出栈的节点为已访问过,遍历root.right,出栈root.right,root.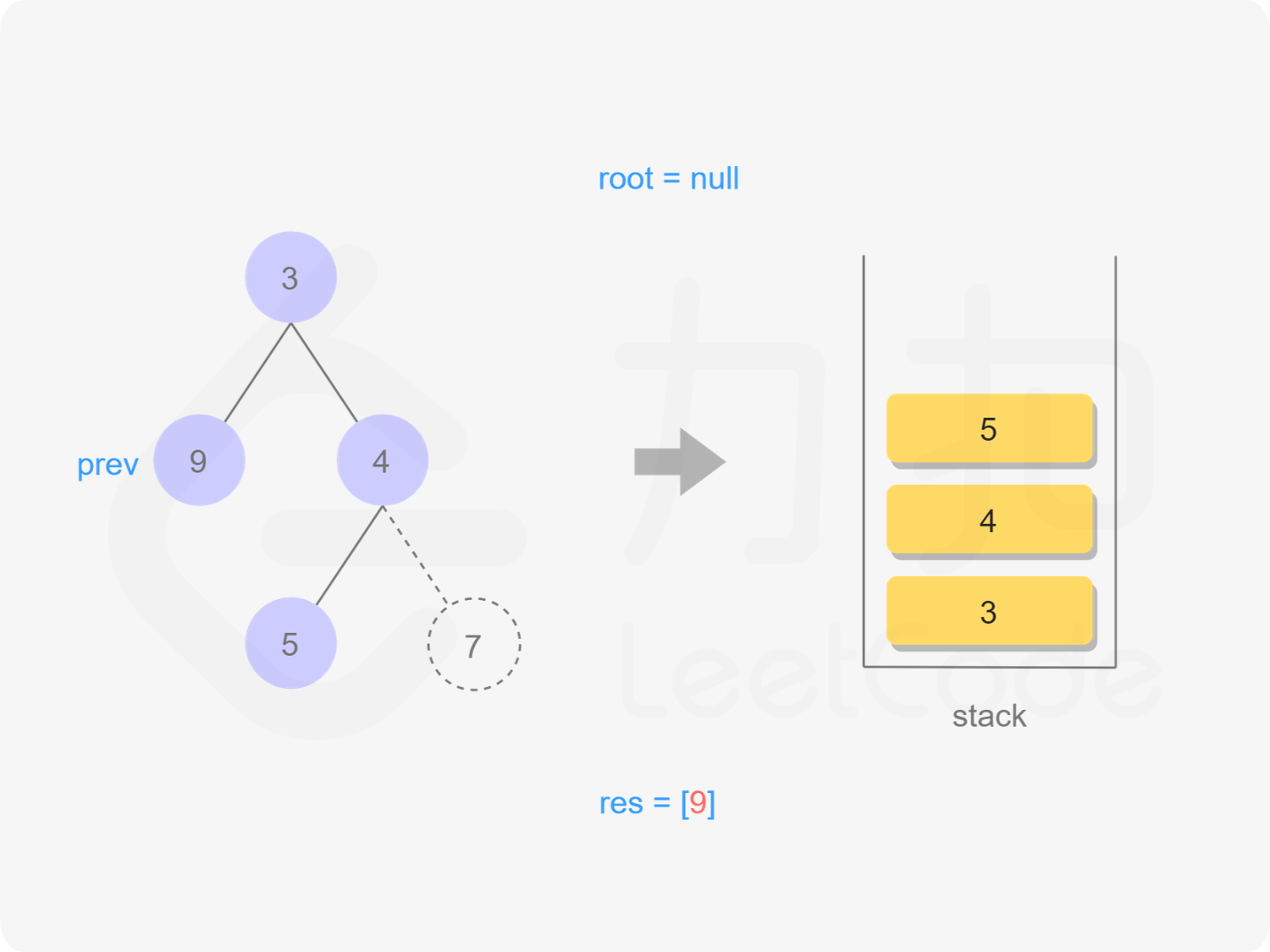
"图9"
5出栈
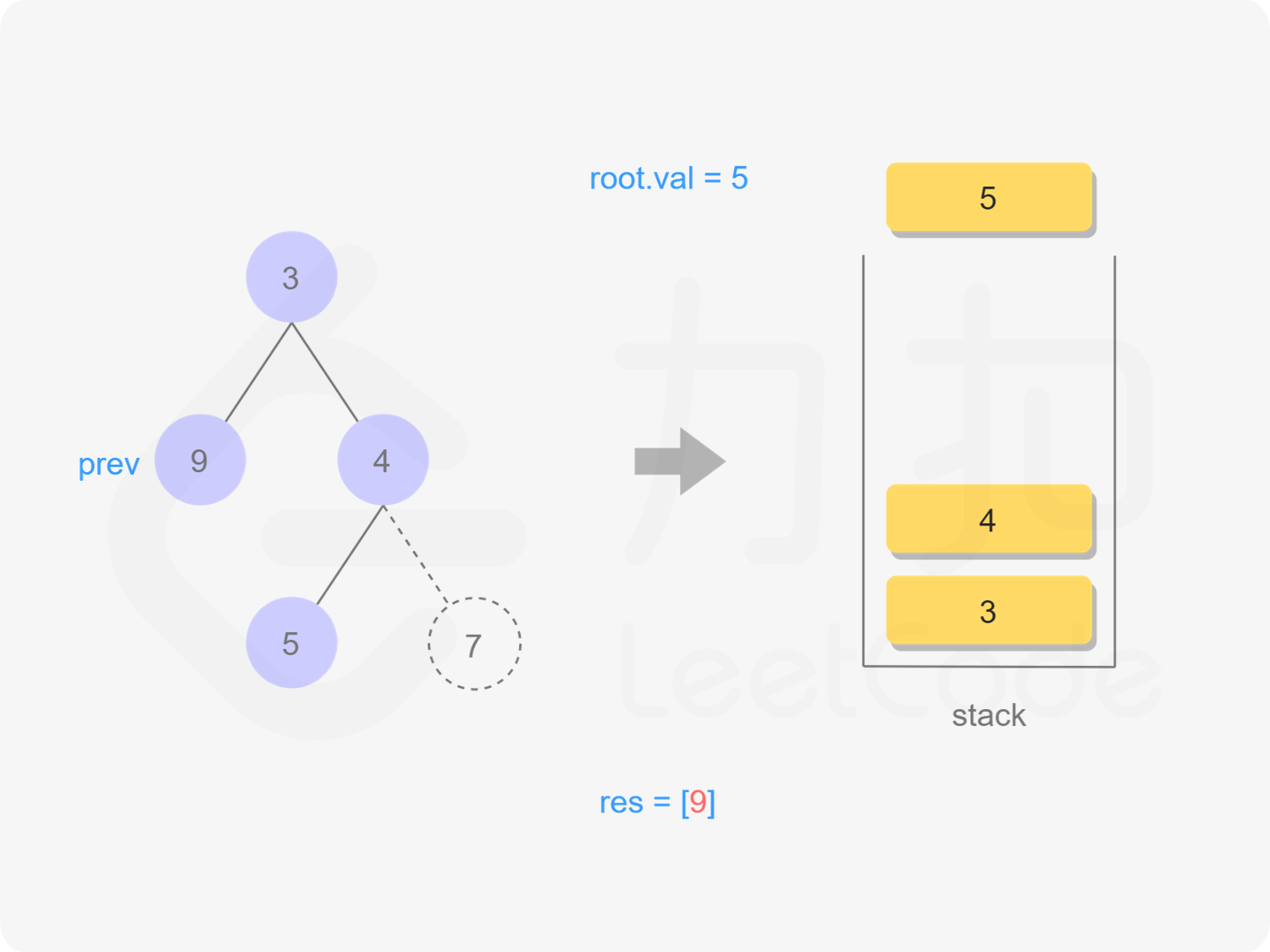
"图10"
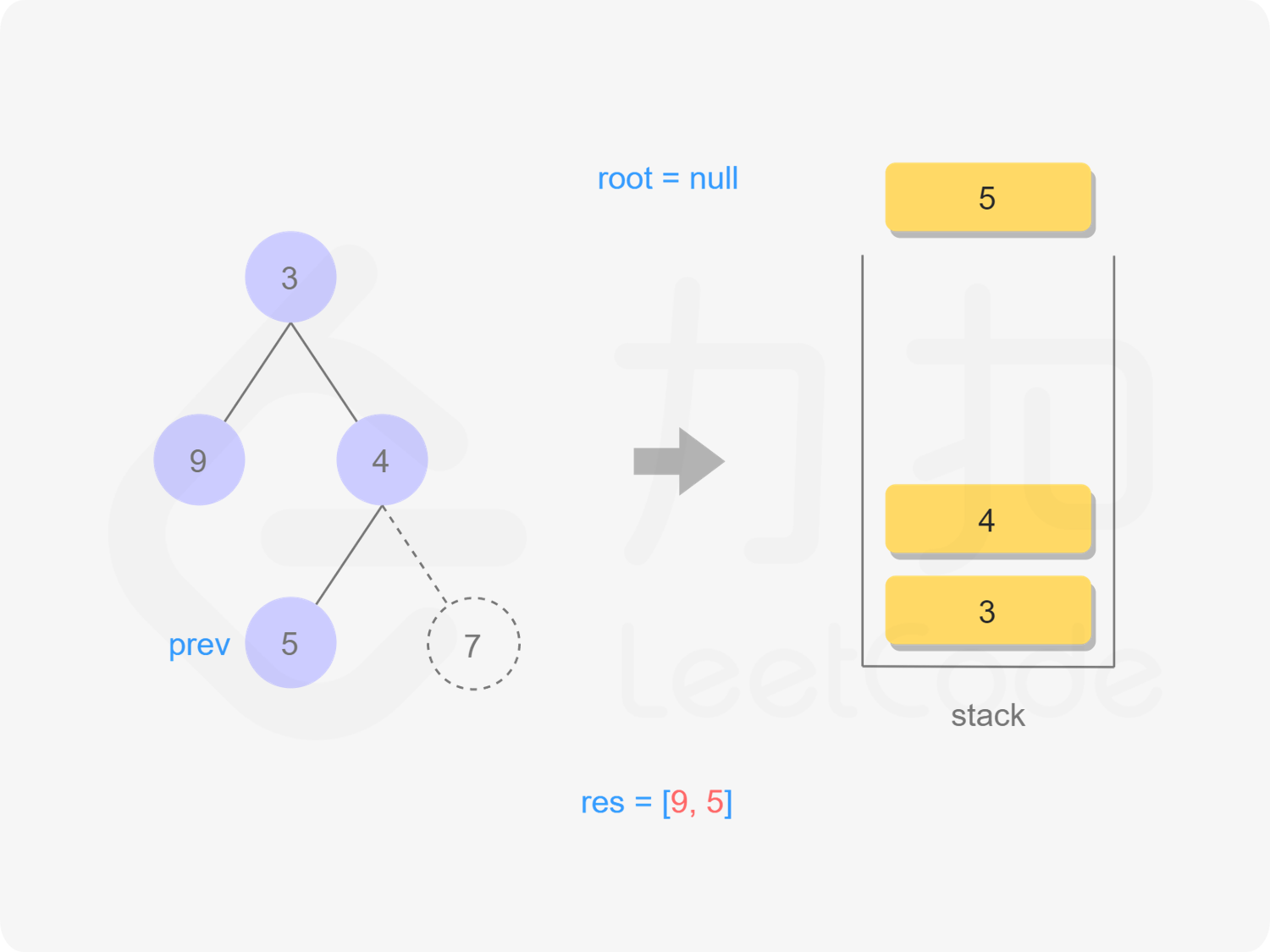
"图11"
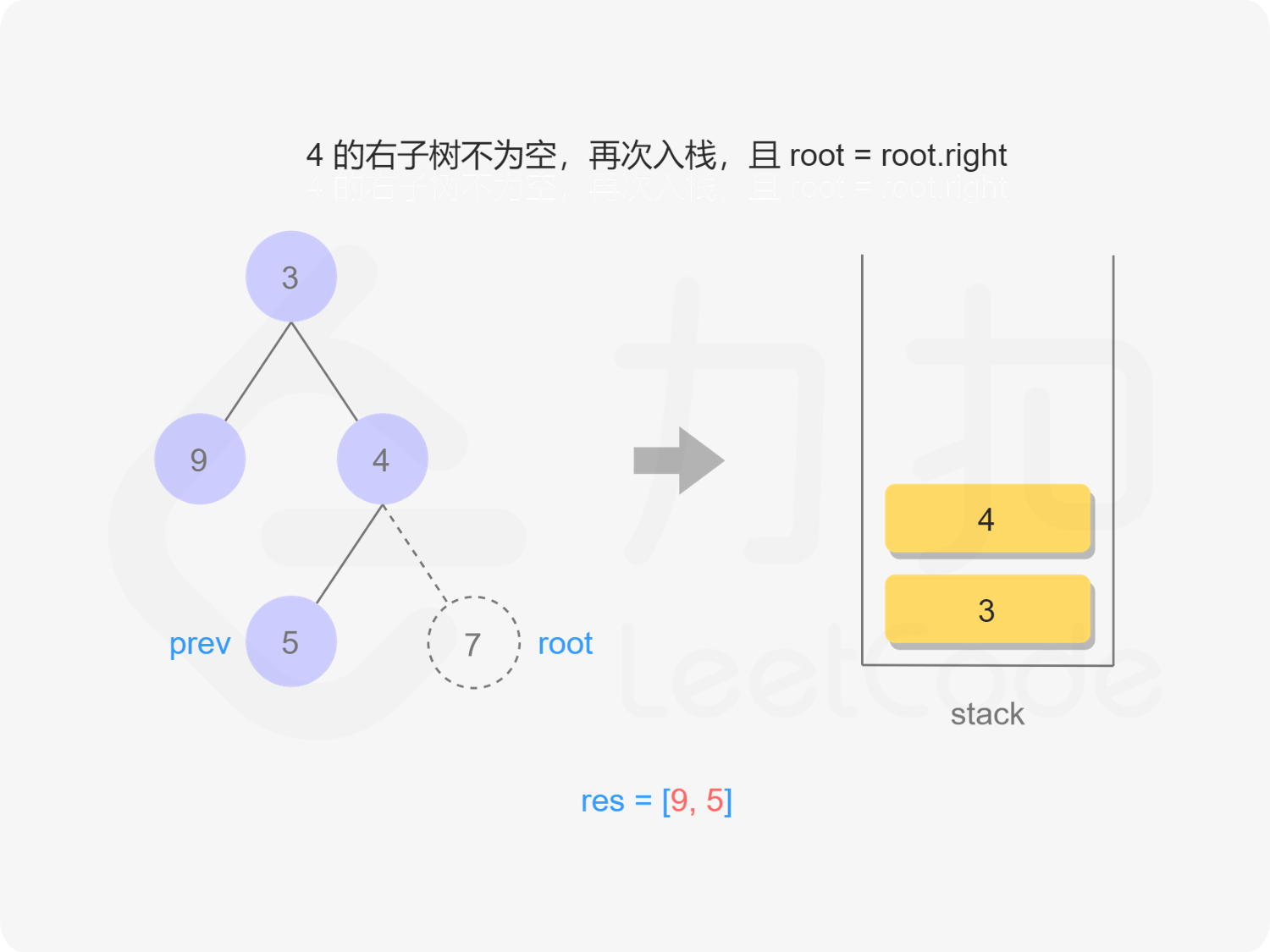
4出栈,但4的右节点存在,入栈4.right
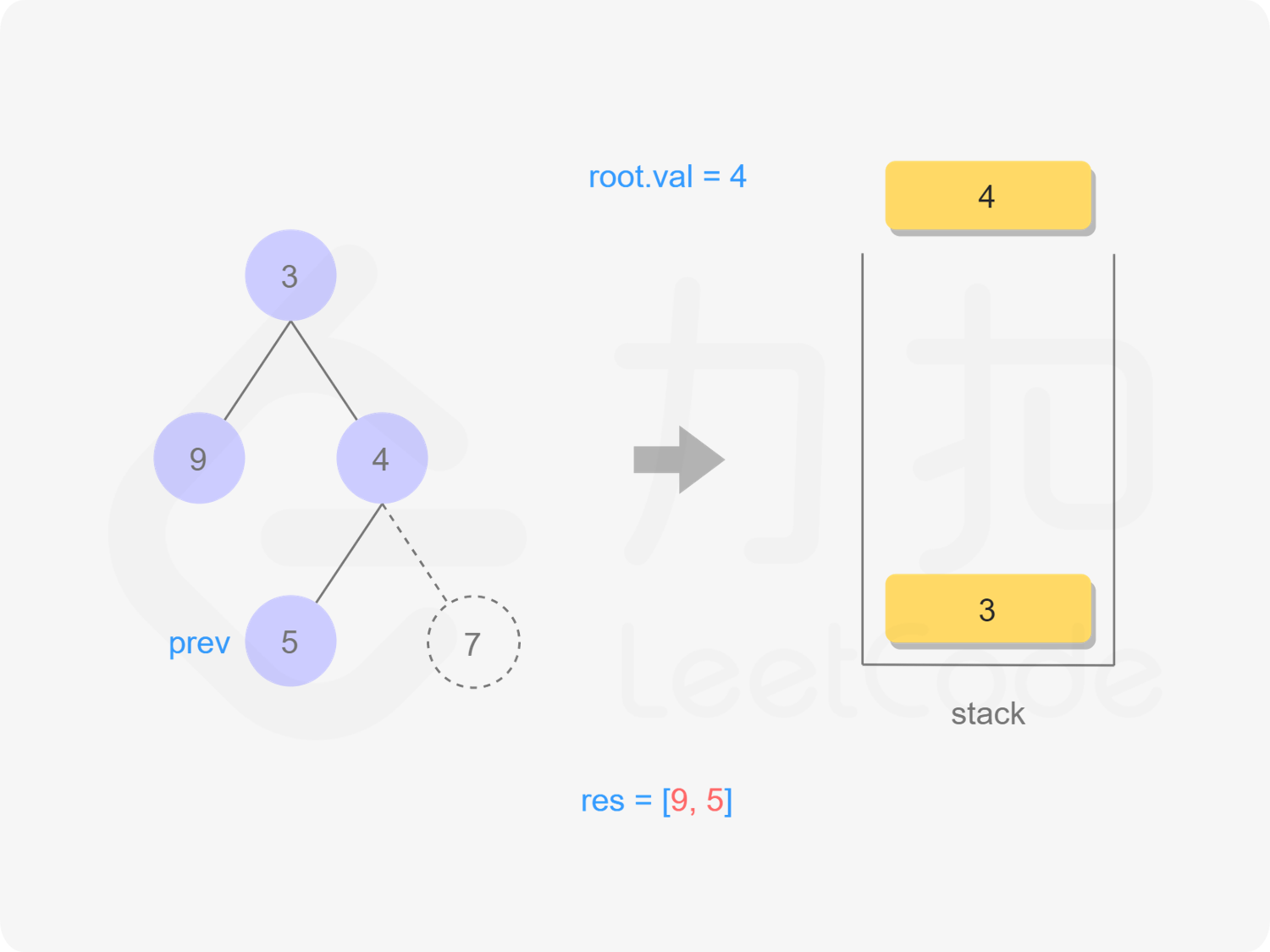
"图12"
"图13"
"图14"
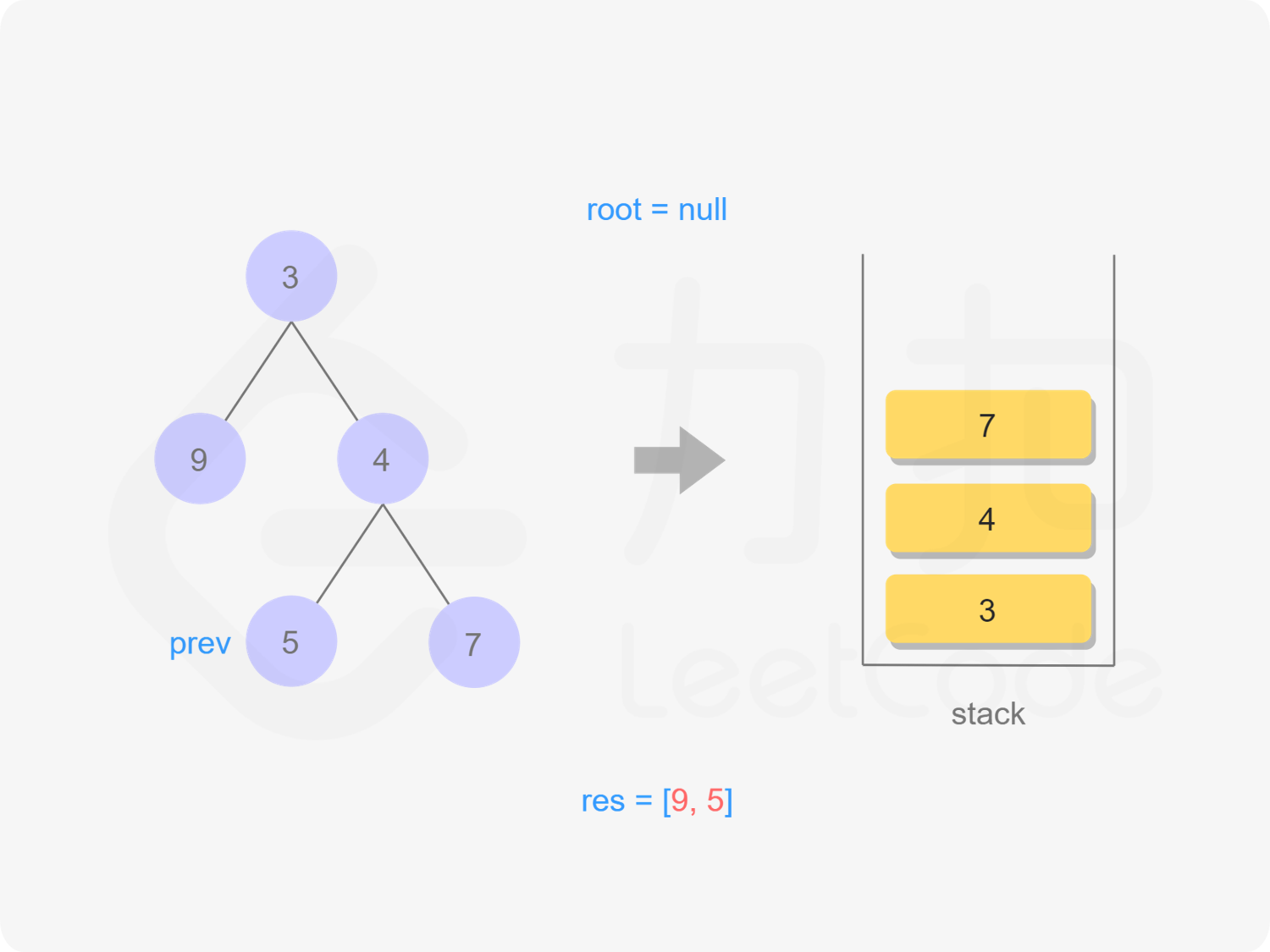
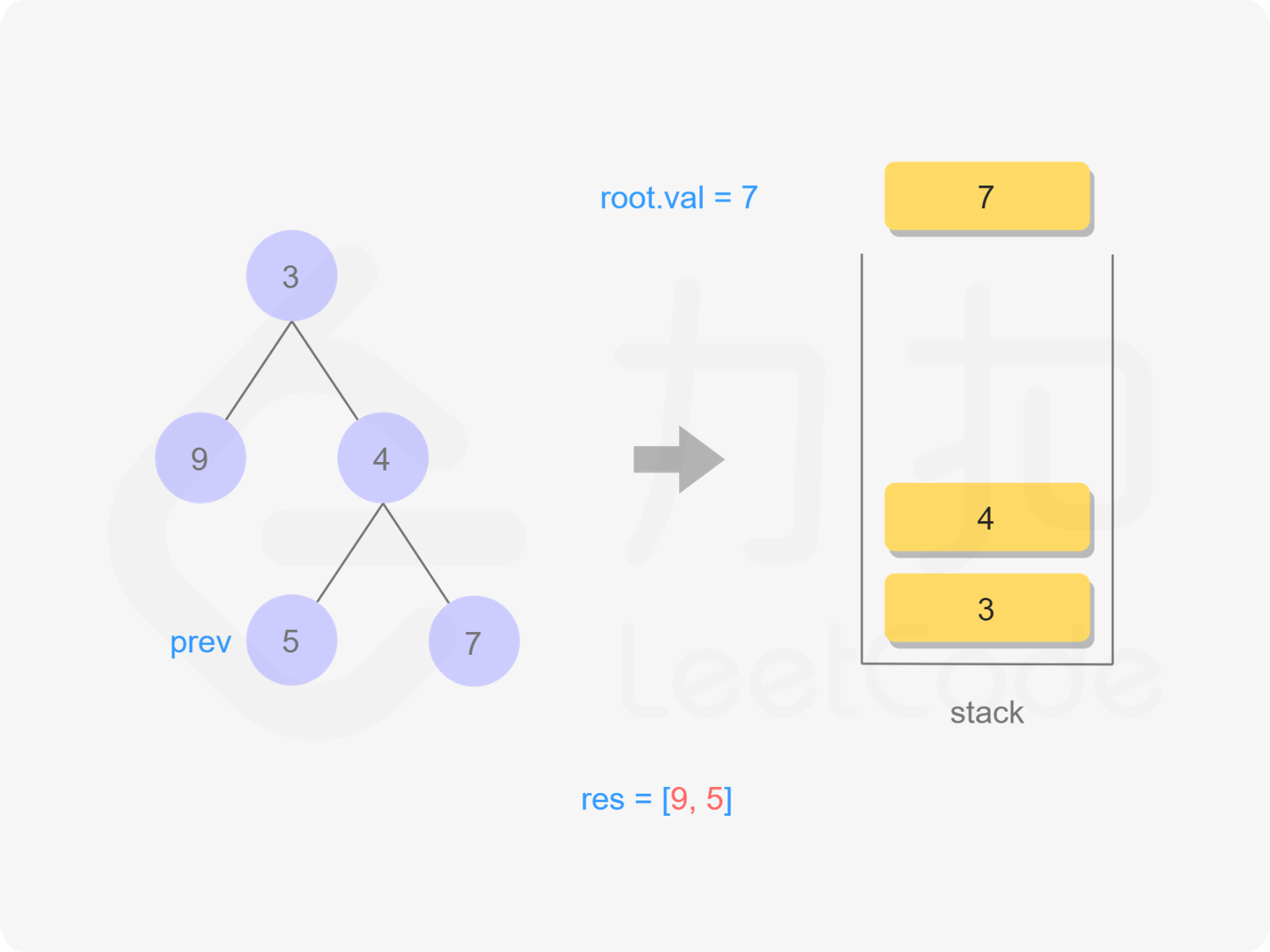
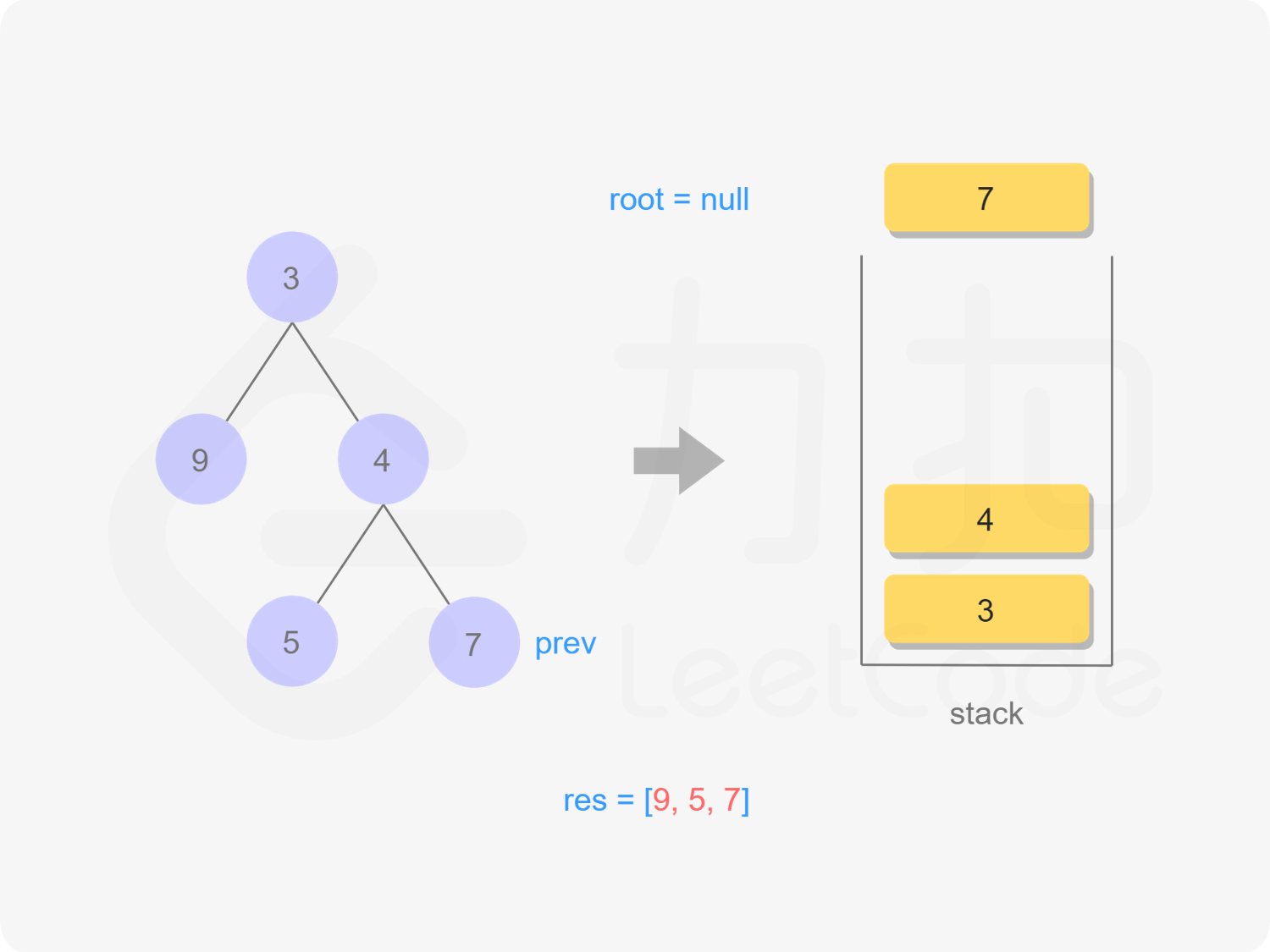
7出栈,遍历,依次出栈4,3,遍历完毕
"图15"
"图16"
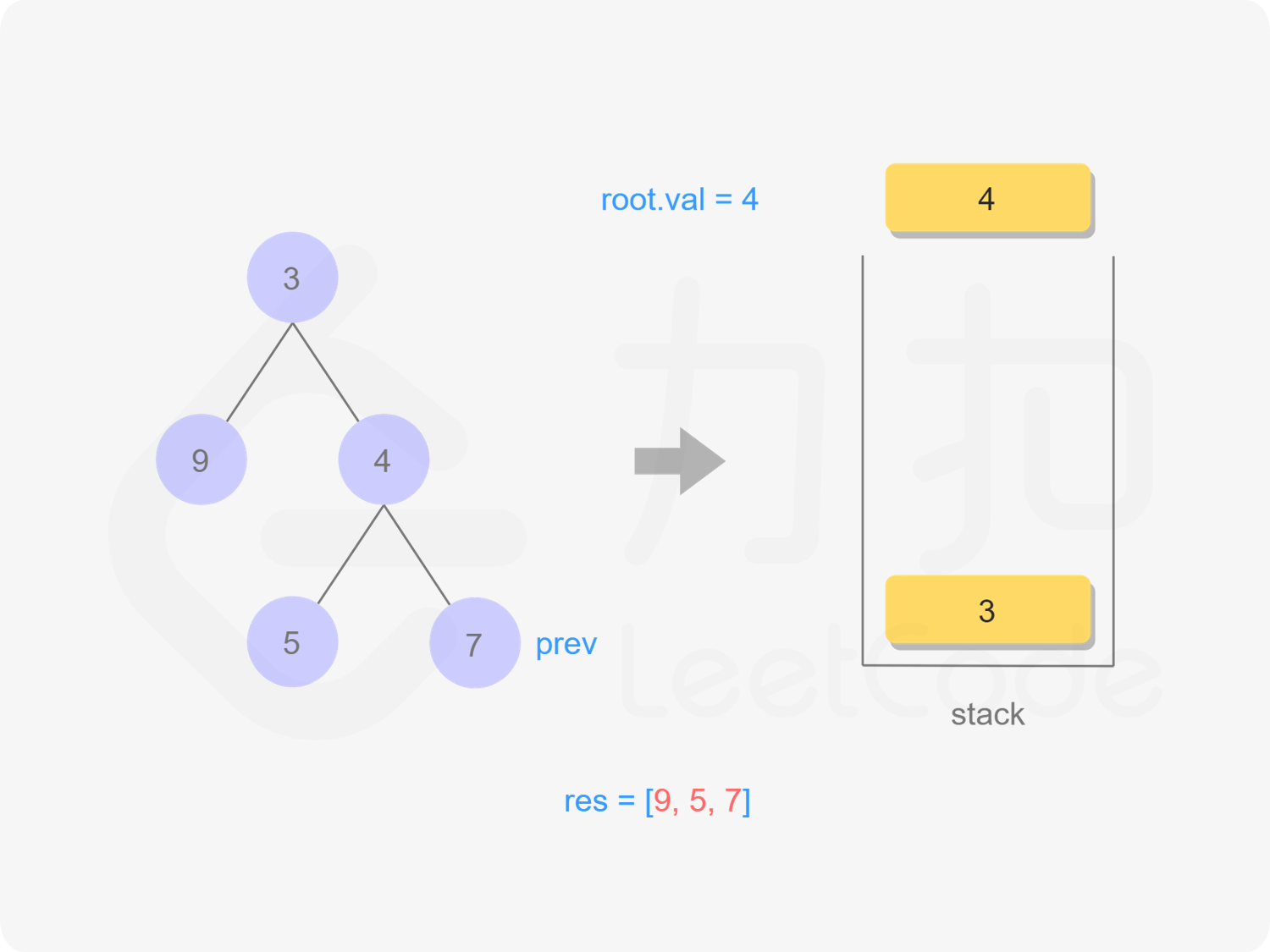
"图17"
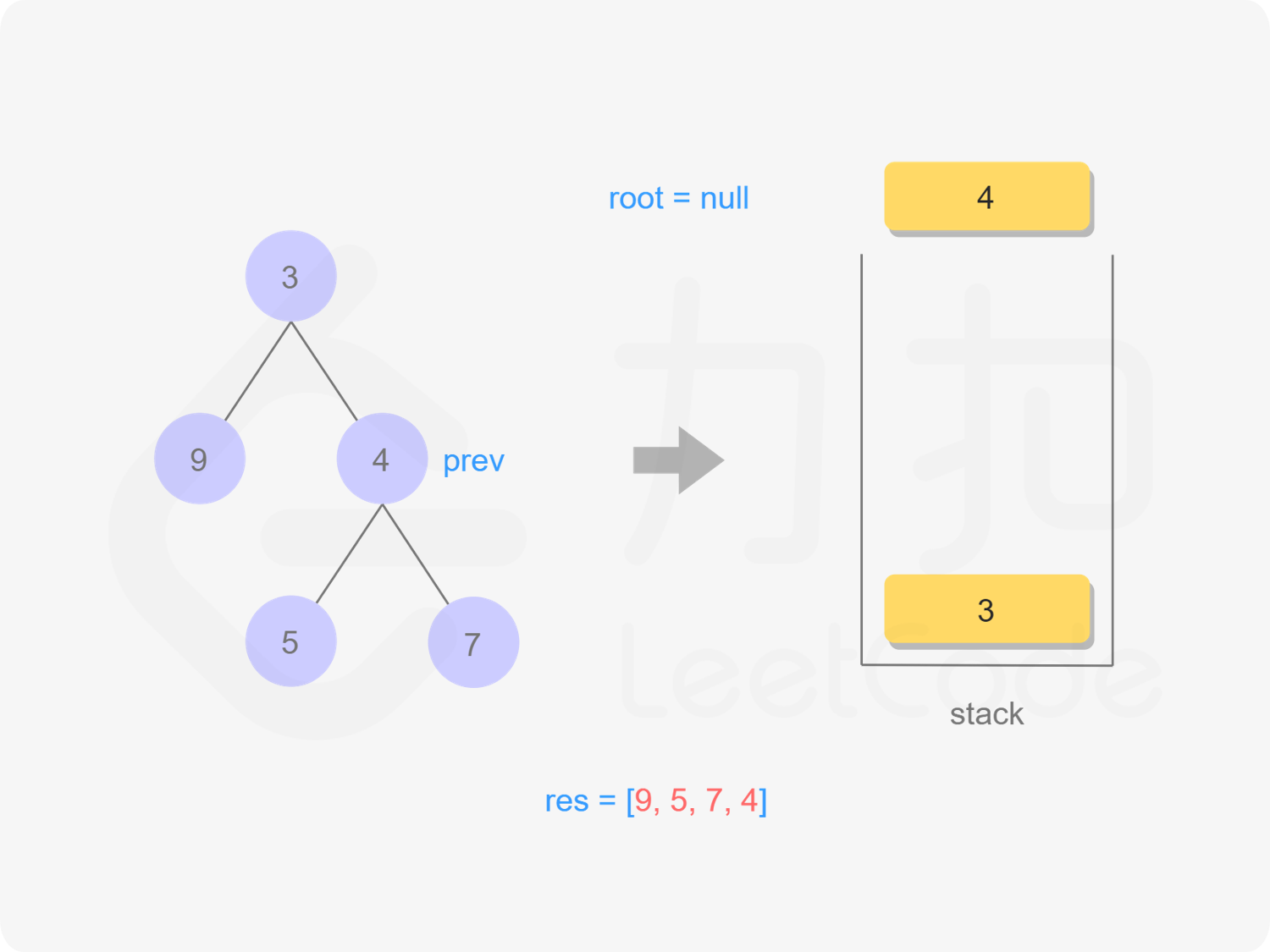
"图18"
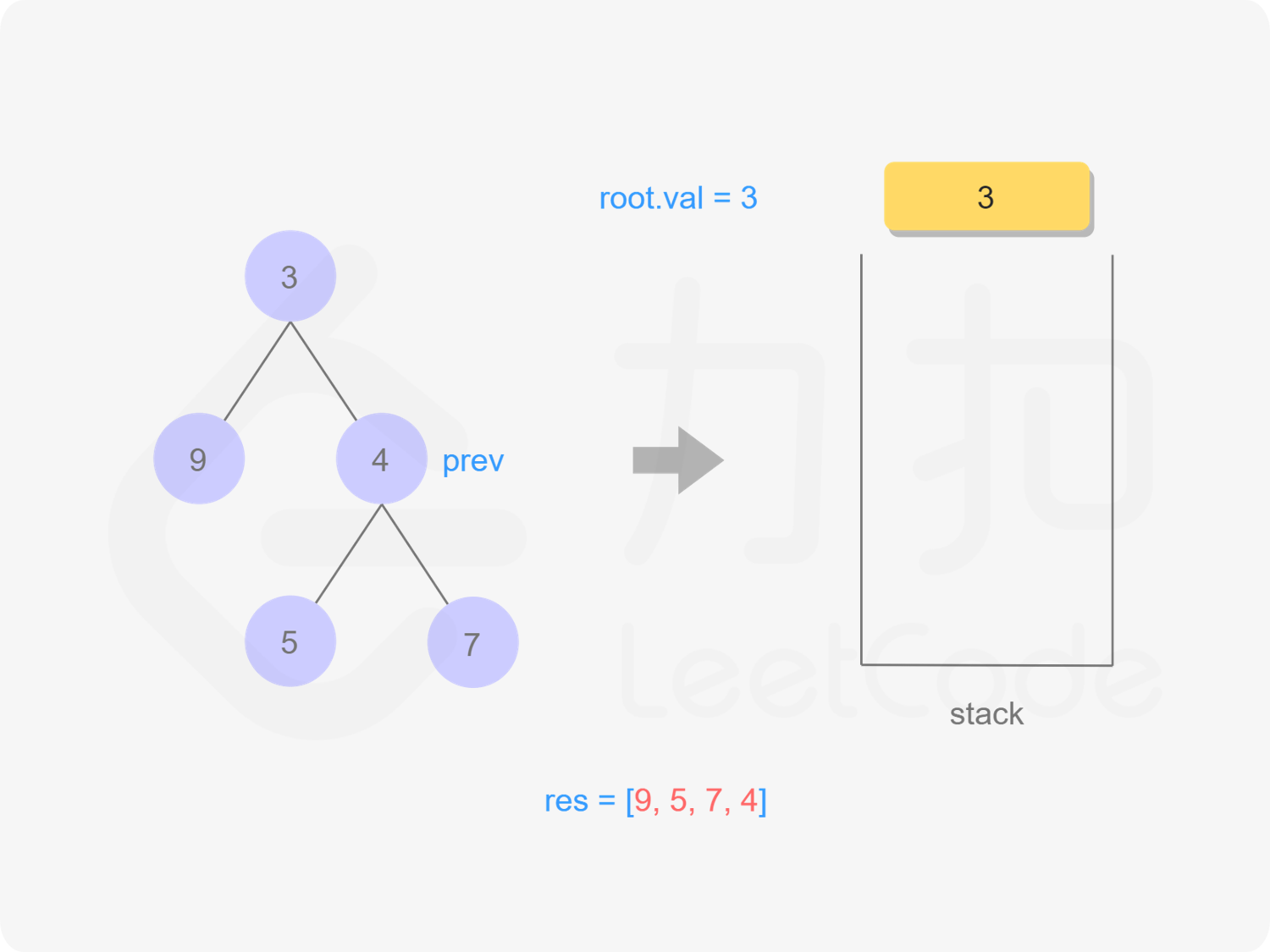
"图19"
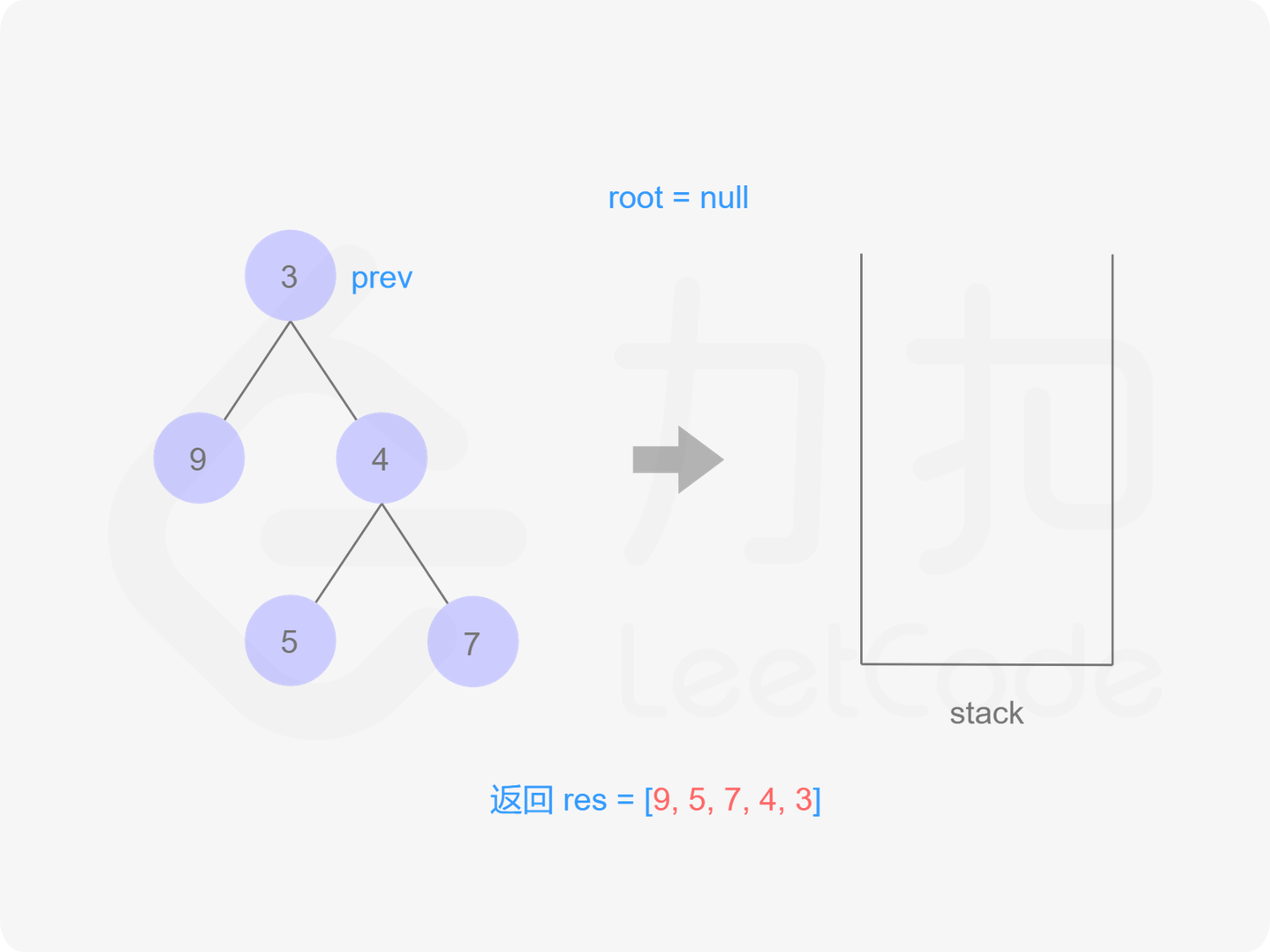
"图20"
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是二叉搜索树的节点数。每一个节点恰好被遍历一次。
空间复杂度:O(n),为迭代过程中显式栈的开销,平均情况下为 O(logn),最坏情况下树呈现链状,为 O(n)。
3.代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
//迭代
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (null == root) {
return res;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode prev = null;
TreeNode current = root;
while (null != current || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (null != current) {
stack.push(current);
current = current.left;
}
//获取当前栈顶节点
current = stack.peek();
//右节点为空,或者已经访问过,则打印,并标记当前出栈的节点为已访问过
if (null == current.right || prev == current.right) {
res.add(current.val);
prev = current;
stack.pop();
current = null;
} else {
current = current.right;
}
}
return res;
}
//递归
public int[] postorderTraversal2 (TreeNode root) {
if (null == root) {
return new int[0];
}
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
postorderTraversal2(list, root);
return list.stream().mapToInt(Integer::valueOf).toArray();
}
public void postorderTraversal2 (List<Integer> list, TreeNode root) {
if (null == root) {
return;
}
postorderTraversal2(list, root.left);
postorderTraversal2(list, root.right);
list.add(root.val);
}
}

